A Brief History of Cooling Water Corrosion Inhibitors
1970s: Chromate
- Effective, non-fouling corrosion inhibitor
- Banned globally because of adverse health effects
1980-1990s: Phosphate and zinc
- Less effective at corrosion inhibition than chromate
- Difficult to control
2000s: Zinc heavily restricted due to aquatic toxicity. Zinc is on the EPA Priority Pollutant and Toxic Pollutant Lists.
2010s: Restrictions on phosphate discharge emerge as a response to its contribution to water body degradation. Phosphate discharge can lead to:
- Algae blooms
- Drinking water contamination with microcystins and THMs
- Eutrophication (sediment accumulation; shifts in flora and fauna)
- Fish kills
- Low dissolved oxygen, causing hypoxic “dead zones”
Phosphate and zinc cooling treatment programs have many other disadvantages:
- Require precise control, balancing phosphate, zinc, calcium, pH, temperature, and polymer
- Effective against steel corrosion, but does not protect copper, aluminum, or stainless steel
- Precipitates with iron and aluminum
Effective cooling tower treatment without zinc or phosphate has not been a practical option, until now.
Introducing FlexPro®
Flexible corrosion inhibitor
Binds directly with metal to form a passive surface
- Treats the metal, not the water
- Not dependent on calcium
- Non-fouling
- Excessive feeding does not cause surface scaling
The inhibitor film it forms is more persistent than a phosphate barrier layer
- Resists corrosion during low-pH excursions and standby
- Effective for steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and copper
Non-phosphorus, non-zinc
Watch a four-day time lapse video that compares a phosphate-based corrosion inhibitor and the FlexPro® program:
Case Study: Raw Water Pond
A southeastern U.S. industrial plant has a pond where some of its treated water is recirculated. When the plant used polyphosphate treatment, the algae growth caused the pond water to turn green. By eliminating phosphate, hypochlorite usage was reduced by 70 percent, and the pond water cleared.
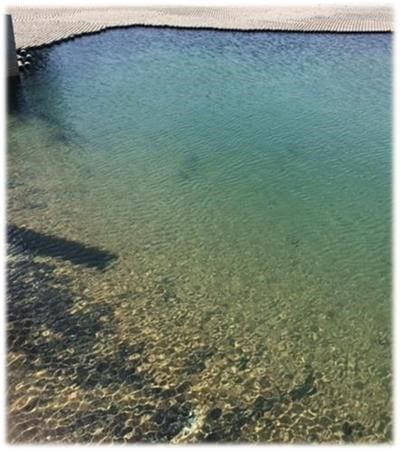


Results are examples only. They are not guaranteed. Actual results may vary.
Other Examples of FlexPro®’s Superior Corrosion Inhibition
Corrosion Rate Reduction at a Steel Mill Before and After FlexPro® Implementation
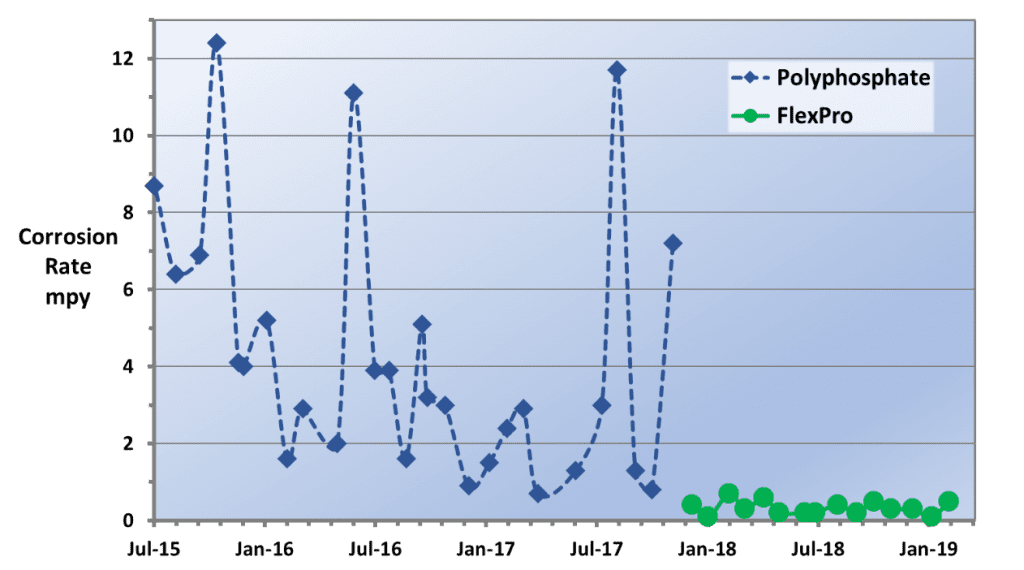
Results are examples only. They are not guaranteed. Actual results may vary.
Protection Against Stainless Steel Stress Corrosion Cracking
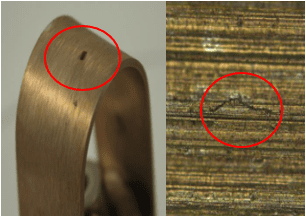
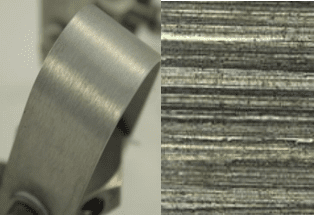
- 304 stainless steel u-bend stressed specimens
- Richmond, Virginia tap water + 1,000 ppm chloride
- 221°F temperature under air pressure
- 15-day duration
Results are examples only. They are not guaranteed. Actual results may vary.
Corrosion Coupon Results


Results are examples only. They are not guaranteed. Actual results may vary.
Click here to learn more.
Please contact ChemTreat for assistance in designing a treatment program customized for your application. Like all other technologies, due diligence is necessary to determine the feasibility for utilizing methods. Always consult your equipment manuals and guides.

